
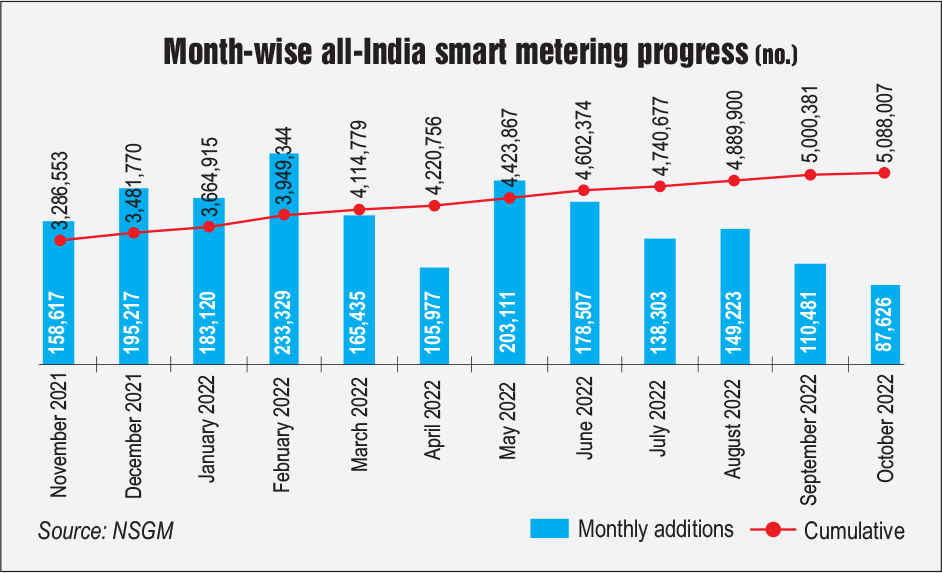
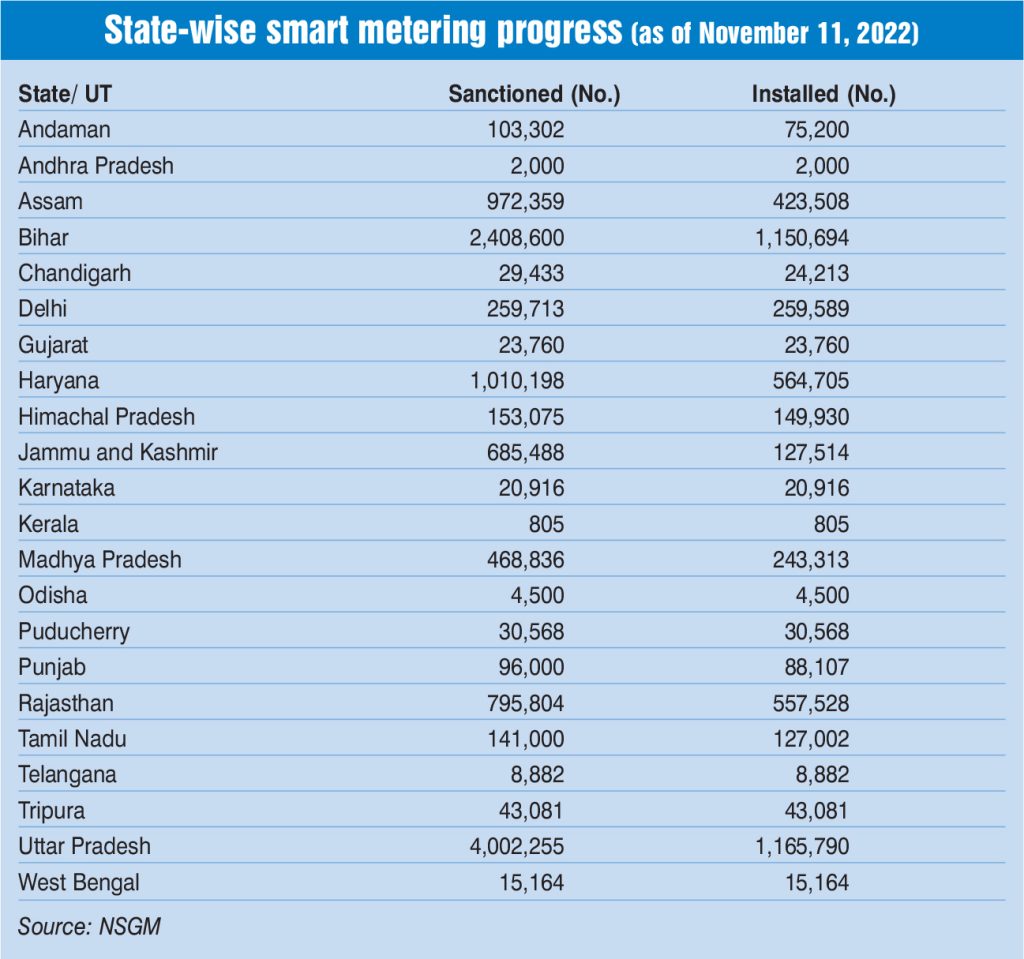
The central government has undertaken various programmes and initiatives for implementing smart meters across the country. In August 2022, the prime minister launched the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS), with an overall outlay of Rs 3.03 trillion, to improve the operational efficiency and financial sustainability of discoms by providing result-linked financial assistance. With the help of this scheme, discoms and power departments will have increased access to funds for prepaid smart metering, distribution infrastructure works and system metering for modernisation as well as loss reduction. The scheme focuses on facilitating the installation of prepaid smart meters for all consumers, along with associated advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and communicable meters for distribution transformers (DTs) and feeders, among other things. The scheme incorporates all current projects sanctioned under programmes such as the Integrated Power Development Scheme (IPDS), the Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY) and the Prime Minister’s Development Package (PMDP)-2015. So far, around 11,275,739 smart meters have been sanctioned across the country and 5,132,368 smart meters have been installed (as per the National Smart Grid Mission [NSGM] dashboard, accessed on November 24, 2022). Additionally, 6,143,371 smart meters are yet to be installed.
Scheme-wise, over 810,250 smart meters have been installed under the IPDS, while 145,268 smart meters have been installed under the NSGM. In addition to this, 130,192 smart meters have been installed under the PMDP and 38,400 under DDUGJY. Among agencies, Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL) has installed 3,107,507 smart meters and REC Power Development and Consultancy Limited has installed 154,406 smart meters. Further, the power utilities have cumulatively installed 1,721,860 smart meters and PFC Consulting Limited has installed 148,595 smart meters.
Government initiatives in metering
Some of the major government programmes are the IPDS, DDUGJY, the Smart Metering National Programme (SMNP) and the NSGM.
IPDS: IPDS, which is aimed at providing 24×7 power supply in urban areas, aims to undertake DT/feeder/consumer metering in urban areas. The programme was launched in November 2014 with a total outlay of Rs 326.12 billion including budgetary support of Rs 253.54 billion from the central government. Metering works under the IPDS entail metering of DTs, feeders and consumers in urban areas and replacement of faulty and electromechanical meters with electronic meters. So far, 95 per cent of the total consumer meters (8.7 million) sanctioned under the IPDS have been installed. The progress rate of system meters is at 92 per cent (total sanctioned: 0.12 million), smart meters at 76 per cent (total sanctioned: 0.16 million) and prepaid meters at 73 per cent (total sanctioned: 0.12 million).
DDUGJY: Launched in December 2014, DDUGJY is targeted at electrification and distribution strengthening in the rural sector, along with metering of DTs, feeders and consumers in rural areas. The scheme has an estimated outlay of Rs 430.33 billion, including a budgetary support of Rs 334.53 billion. A total of 16.6 million consumer meters have been sanctioned under the scheme and 3 per cent are yet to be installed. In the case of 11 kV feeders, 244,000 meters have been sanctioned, of which 43 per cent are yet to be installed. In the case of DT meters, 306,000 have been sanctioned, of which 28 per cent are yet to be installed.
SMNP: EESL is implementing the SMNP with a target to replace 250 million conventional meters with smart meters. The programme is being implemented by EESL through demand aggregation, bulk procurement and monetisation of savings. Recently, EESL and the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund have formed a joint venture, IntelliSmart Infrastructure Private Limited, to implement, finance and operate the smart meter roll-out programme for discoms. Of nearly 12 million smart meters under implementation across the country, EESL is engaged in the installation of 80 per cent. So far, nearly 1.4 million smart meters have been installed by EESL.
NSGM: Various smart grid pilot projects are under way under the NSGM. AMI is a key component of projects under the NSGM. Currently, five smart grid projects have been sanctioned under it. Apart from these programmes, the central government has asked the states to move towards smart prepaid metering in three years. The Union Budget 2020-21 also focused on smart metering by utilities. Recently, the long-standing standard bidding documents for totex projects for smart prepaid meters have been finalised, which is a major achievement. They are now available on the NSGM website. In addition, options for a common back-end infrastructure facility for AMI projects are being explored.
Recent developments
Recently, the Ministry of Power issued the country’s largest ever tender for procuring 10 million smart meters. Close to a dozen meter manufacturers and leading power sector conglomerates have participated in the pre-bid meetings and are likely to submit interest for the same. This includes the Adani Group, Larsen & Toubro Limited, Robert Bosch, EdF, Tata Power, India Power, and Ashoka Buildcon. Leading meter makers such as Landis+Gyr, Schneider, Secure Meters, Anvil Cables and Avon have also participated in the pre-bidding discussions and are likely to place bids. Reportedly, the first phase of the tender is for the procurement of 2.5 million meters, which will be installed in the central and western regions of the country. The tender has been floated by the Power Grid Corporation of India for installing AMI projects.
In October 2022, leading energy and infrastructure players including L&T, the Adani Group and the GMR Group have placed bids for one of the largest deployment of smart meters in Uttar Pradesh. IntelliSmart, a joint venture of EESL and the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund, has also shown interest. The Rs 230 billion tender is to install 28 million smart meters across the state. These smart meters will be installed in the areas of four of the five power distribution companies in Uttar Pradesh, namely, Purvanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited, Pashchimanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited, Dakshinanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited and Madhyanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited. This covers the entire state except the area under Kanpur Electricity Supply Company Limited. At the same time, EESL has completed the installation of over 3 million smart meters in Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC)-Delhi, Bihar, as well as the union territory (UT) of the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, under the SMNP. The company has signed agreements with the state designated agencies and utilities in these regions for the large-scale deployment of smart meters. It further aims to install a total of over 4.7 million smart meters by December 2023. Recently, EESL completed the installation of over 1.05 million prepared smart meters in Bihar. The company has also installed around 1.16 million smart meters in Uttar Pradesh, over 124,000 in Rajasthan, over 530,000 in Haryana, around 64,000 smart meters in NDMC-Delhi and over 74,000 in Andaman. EESL has taken internet of things services from BSNL, Jio and Vodafone Idea for network connectivity in discoms. It is also working in association with L&T, Robert Bosch and EDF Energy, which provide unique system integration solutions.
The smart meter roll-out is part of the central government’s newly launched power distribution reforms scheme. The Rs 3 trillion Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS) aims to improve the operational efficiencies and financial sustainability of state-owned discoms/ power departments by providing conditional financial assistance. The scheme has an outlay of around Rs 3 trillion with an estimated gross budgetary support from the central government of Rs 976.31 billion. Of this, Rs 100 billion has been allocated for smart metering infrastructure across the country. Government estimates indicate deployment of 250 million smart meters for domestic consumers. The RDSS envisages smart metering in the opex mode and provides financial support to discoms opting for prepaid smart metering.
The way forward
The distribution utilities are revamping their metering infrastructure in a big way, with the adoption of smart meters to improve their operational and financial performance. Going forward, smart meter installation is expected to pick up pace, bolstered by the central government’s impetus.
