Since its incorporation in June 2014, Southern Power Distribution Company of Telangana Limited (TSSPDCL) has been working towards strengthening and expanding its distribution network to ensure reliable and uninterrupted power supply to its customers. The utility has been working on grid modernisation and has been leveraging technology to optimise its operations. It has been at the forefront of undertaking network and asset management and implementing smart grid initiatives. Through these, the utility has managed to significantly improve its operational and financial performance and lower distribution loss levels.
Network growth
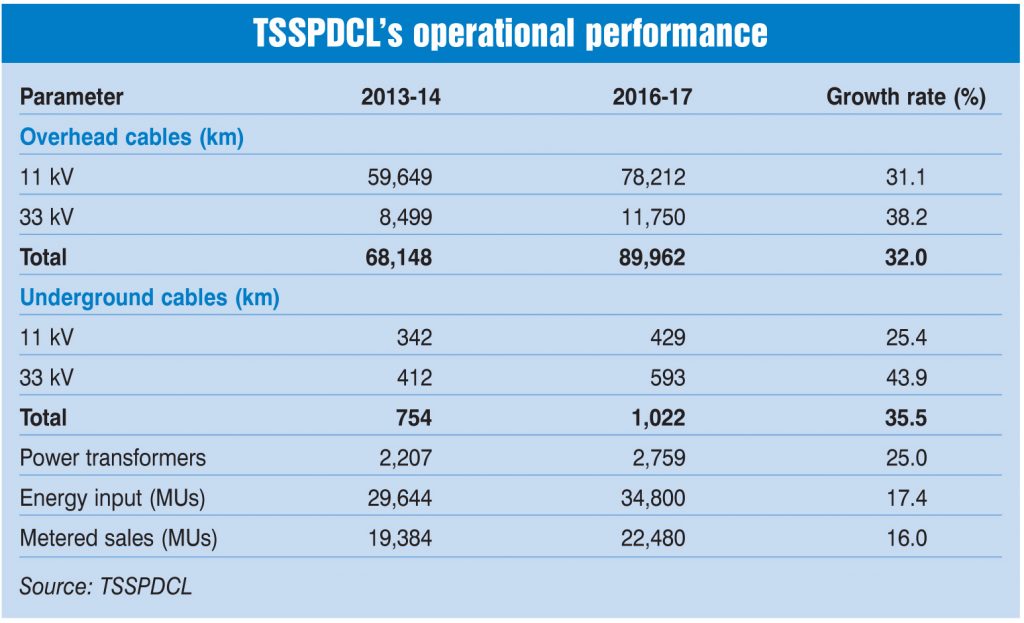
Between 2014 and 2017, the discom’s overhead line length at the 11 kV and 33 kV levels grew at 32 per cent to reach 89,962 km, the underground line length at the 11 kV and 33 kV levels at 35.5 per cent to reach 1,022 km, and the low tension (LT) network at 14.31 per cent to reach 176,000 km. As of October 2017, the company operates 2,759 power transformers and 365,691 distribution transformers (DTs). Further, the discom operates 1,453 substations across voltage levels. Its network comprises 6,177 feeders at the 11 kV level and 1,039 feeders at the 33 kV level including 160 dedicated feeders at the 33 kV level that cater to industrial needs.
Operational and financial performance
The utility has recorded a reduction in the average cost of supply (ACS)-average revenue realised (ARR) gap. In the first quarter of 2017-18, TSSPDCL recorded an ACS-ARR gap of Re 0.30 per unit against Re 0.75 in 2015-16. The annual per capita consumption in the discom’s distribution area increased from 1,276 units in 2013-14 to 1,401 units in 2016-17. In addition, the utility’s energy input increased from 29,644 MUs to 34,800 MUs while metered sales increased from 19,384 MUs to 22,480 MUs during the same period.
The discom also witnessed a reduction in distribution losses, which came down from 12 per cent in 2013-14 to 10 per cent in 2016-17. Meanwhile, its DT failure rate reduced from 13 per cent to 9.84 per cent and the power transformer failure rate declined from 2.79 per cent to 1.74 per cent during the same period.
Network and asset management
One of the key initiatives taken by the discom is network and asset management. TSSPDCL has implemented the high voltage distribution system (HVDS) for the agricultural sector, which has resulted in a substantial decline in loss levels. This has also led to a significant reduction in the number of unauthorised agricultural connections. For better decision-making, the utility has formulated a root-cause analysis framework (through brainstorming, Pareto analysis and fishbone analysis) to analyse instances of leakages and outages, and to effectively mitigate them. Besides this, the discom uses thermal imaging cameras to detect hotspots in the network. Through preventive maintenance, the discom has managed to significantly scale down the DT failure rate.
SCADA and DMS
TSSPDCL has set up supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems at 228 substations in the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) area. It is currently in the process of implementing SCADA systems across all its substations. It is also setting up distribution management systems (DMSs) for 156 feeders at the 11 kV level in the GHMC area. The DMS is envisaged to be a decision support system to assist control room and field operating personnel in system monitoring and control in an optimal manner. It will allow the utility to identify points of excess load and resolve the issue. The SCADA and DMS implementation has enabled the discom to monitor power flow, manage load growth, undertake operations and maintenane (O&M) of the network, isolate fault locations and undertake service restoration through feeder reconfiguration, distribution load forecasting, seamless data exchange and network connectivity analysis.
Smart grid pilot
TSSPDCL has conducted a smart grid pilot in the Jeedimetla industrial development area in Hyderabad. The project covers 12,000 consumers and envisages functionalities such as advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) for the residential and industrial areas, peak management, outage management and power quality. The pilot project has delivered an improvement in billing efficiency and a reduction in transmission and distribution (T&D) losses. The smart grid architecture for the project comprises host stations, data control centres and DMS. The smart meters function through the Zigbee communication network and are connected to application servers that are used to interpret the data.
Smart metering
The utility is setting up smart meters in its distribution area. It is deploying both prepaid and post-paid smart meters with remote connect/disconnect facility, remote meter upgrades and remote tamper alerts. Infrared data association (IRDA) meters have been installed for approximately 68 per cent of the metered consumer base. The meters enable a two-way communication with consumers and the utility, and can be utilised for peak load management, load profiling and remote monitoring. The information on all parameters is transferred to the central host stations where the data is analysed to make inferences and resolve issues.
Consumer-centric measures
The utility has implemented several consumer-centric measures. It has set up a number of call centres that are connected to a centralised call centre for consumer grievance redressal. The discom is planning to introduce virtual call centres wherein complaints would be forwarded to the call centres through the web. These calls would then be directed to the respective local call centre to ensure that the complaints are addressed in a timely manner.
In addition, the discom has undertaken steps to improve the billing efficiency of its consumers. Of a total base of 7 million consumers, 2.9 million consumers have been connected to the IRDA port for billing purposes and this has resulted in a considerable decrease in the commercial losses of the company. Moreover, 100 per cent of LT billing is being carried out by spot billing machines. Collectively, IRDA ports and spot billing have enabled the discom to achieve 100 per cent billing efficiency. Currently, 35-40 per cent of bill collections every month are facilitated through the digital platform. The utility has also launched an application to simplify the billing procedure for consumers.
In addition to these, TSSPDCL has undertaken a series of IT initiatives. The mobile application, for instance, is being utilised for reliability and end-to-end outage management in the GHMC area. The utility plans to extend this to the entire TSSPDCL distribution area. The company has also developed a web portal, which consists of a dashboard with information on revenue collection, billing, general reports, consumer analysis tool reports and ledger reports. The dashboard also features an energy audit portal that indicates the point of pilferage and helps in the timely detection of faults.
The recording of a huge quantum of data has necessitated the discom to develop tools to analyse the data. These tools are being used to manage operations optimally. TSSPDCL has been utilising data for increasing productivity and improving outage response through situational awareness. In addition, the discom is using data analytics to cut down its O&M expenditure and thereby enhance its savings. Analysing data has also enabled the utility to develop a greater connect with consumers and design new products and services that cater to the specific needs of different consumer groups. This understanding has enabled TSSPDCL to implement demand-side management programmes.
To conclude, TSSPDCL’s efforts to modernise its network have helped bring in improvements in its operational performance and consumer satisfaction.
Based on a presentation by Kamesh, Superintending Engineer, O&M, TSSPDCL