 By Sanjay Banga, President, Transmission & Distribution, Tata Power
By Sanjay Banga, President, Transmission & Distribution, Tata Power
Geographic information systems (GIS) are deployed by utilities for mapping and bringing location reference to their network assets, which are spread across the geography. The traditional use of GIS has evolved in the past few years. The advancement of computer and communication/mobility technology has brought GIS out of the boundaries of four walls and taken it beyond asset geo-referencing systems.
Business challenges
The majority of utility businesses are required to work within the framework of regulations. The competitive environment brings forth another dimension for Tata Power Mumbai Distribution operations. The competitive and regulated tariff structure makes Tata Power spend every penny strategically, as it has direct or indirect impact on tariff. The application of technology has now become a basic requirement. Appropriate and thoughtful technology selection, effective implementation and sustainability of deployments with continual improvements are some of the critical factors.
Implementation
The advancement in GIS has enabled mass-market applications based on web enabled location-based services (LBS). Cab aggregators, delivery chain services, consumer marketing, etc. are some day-to-day examples of the enormous power of GIS for achieving innovation with excellence in operations and productivity. Along with traditional uses, Tata Power has strategically undertaken similar utility-focused innovations on its GIS platform, which are not only a differentiator from conventional utility GIS but have gone much beyond and are proving to be a key technology enabler in the challenging environment.
Key challenges during implementation and their mitigation:
- Being the most data dependent IT system, GIS faces the challenge of having up-to-date data from the quality-quantity point of view. Data quality consists of accuracy and timely data update. Moreover, accelerating the data readiness for other enterprise systems such as DMS, network analysis system, and ERP is a daunting task. Tata Power has embedded GIS into various processes. Further, seamless integration with other systems such as ERP and mobility platform has helped improve GIS data quality and quantity as well as the productivity of other functions.
- GIS technologies initially faced acceptability issues among users, especially traditional utility employees/users. With continuous awareness sessionsdemos/trainings, numerous use-case demonstrations for many of their business difficulties, involving users at the design stage, helped improve the confidence level of users. The development of many GIS-based and diverse user-specific small-big utility tools empowered users and also helped in making their job easy and meaningful; this ultimately created ownership and trust for GIS.
- GIS for utilities is a typical technology where GIS knowledge and utility knowledge go hand in hand. Tata Power has brought together GIS professionals and utility professionals in its GIS team. This has helped in creating synergy and cutting-edge capabilities for the GIS team as a whole. The team is able to give comprehensive solutions for internal and external users/customers.
- Managing up-to-date data, and ensuring user friendly access to system and its solutions was a challenge in moving forward along with cybersecurity framework. A regular review and other security measures were taken and validated from time to time using tests such as vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT).
Success factors
- Deploying a standard and strong utility GIS software platform and leveraging its capabilities through the deployment of different out of band (OOB), small and big customised developments to meet diverse user and business requirements is one of the key factors for success.
- Deriving innovative combinations of OT and GIS system capabilities, Tata Power GIS has become a real-time system vis-a-vis a static or offline system. “Mobile-GIS assisted system for Restoration & Care (maRC)” is a typical example where Tata Power has in-house developed and deployed a comprehensive digital and automated cost effective system for the complete “customer trouble call management” process.
- Different distribution activities such as planning, execution, operations, and result analysis are now done more scientifically and are giving an overall edge in functioning. Stress on in-house development and the re-use of existing systems have made GIS not only a useful technology but also a cost-effective solution to many distribution challenges.
- GIS is maximising the benefits of its capabilities for numerous distribution functions and is impacting many processes (65 per cent enterprise processes) in distribution such as customer acquisition, connection management (MCS), meter reading, network planning, RR, complaint management, optimisation of CRC and BCC locations, and cable route patrolling management (SPINe). Currently, GIS is supporting more than 25 different functions of distribution with business-specific customised applications, and in-house analytical tools, which have been developed from time to time. GIS has evolved as a single source of truth and is no more a “support system”. It is now a hygiene factor for distribution. A cross-section of use cases has helped understand its impact on the early return on investment (ROI) of the expenditure incurred on this technology apart from other benefits. (Fig. 1)

A team having the correct mix of cross domain experts is used by Tata Power for going much beyond the conventional GIS use. Tata Power’s expertise in GIS and its capabilities for its wider implementation present opportunities for future business growth, as GIS is now becoming an integral part of new businesses and the day-to-day life of progressing utilities. (Fig. 2)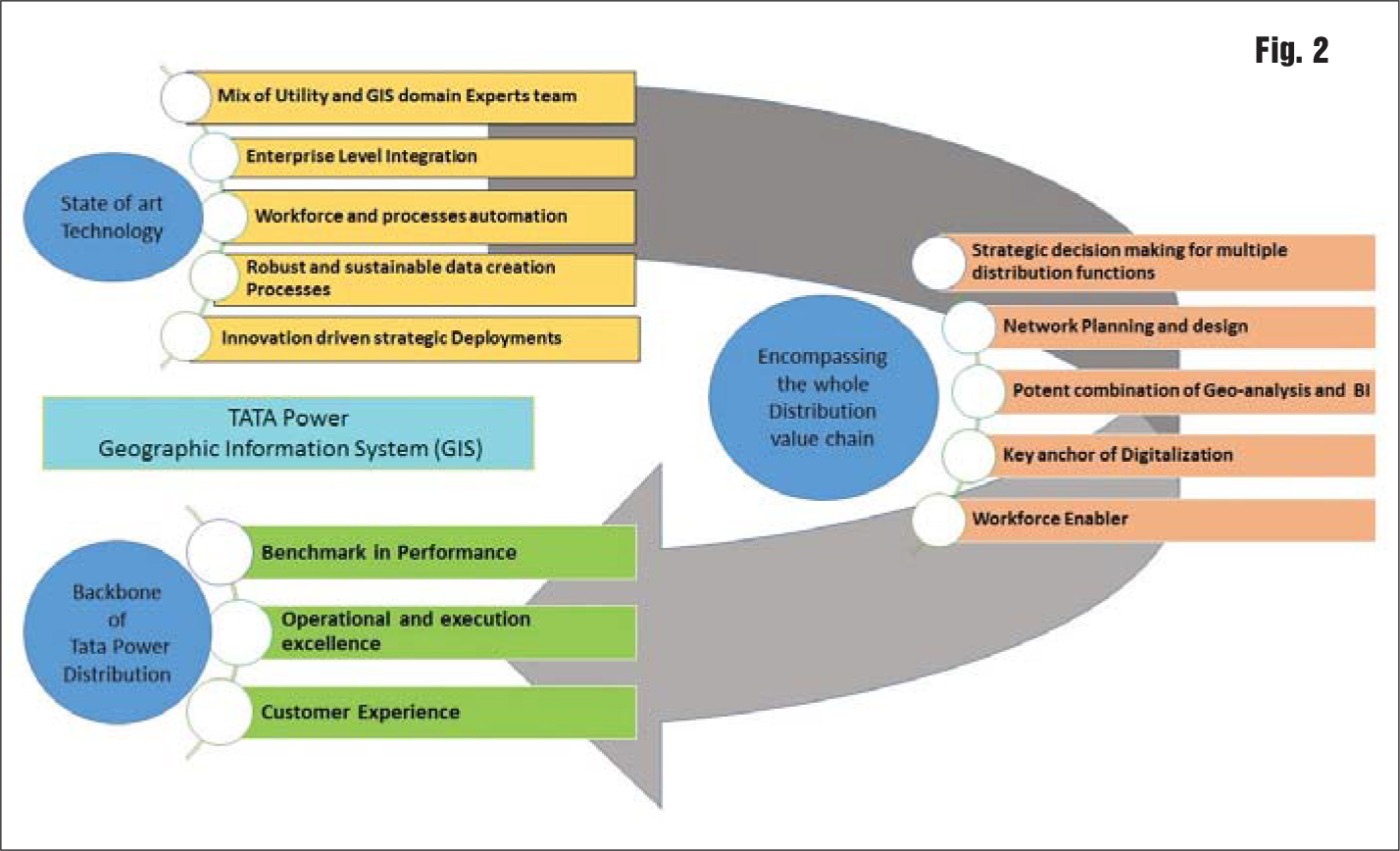
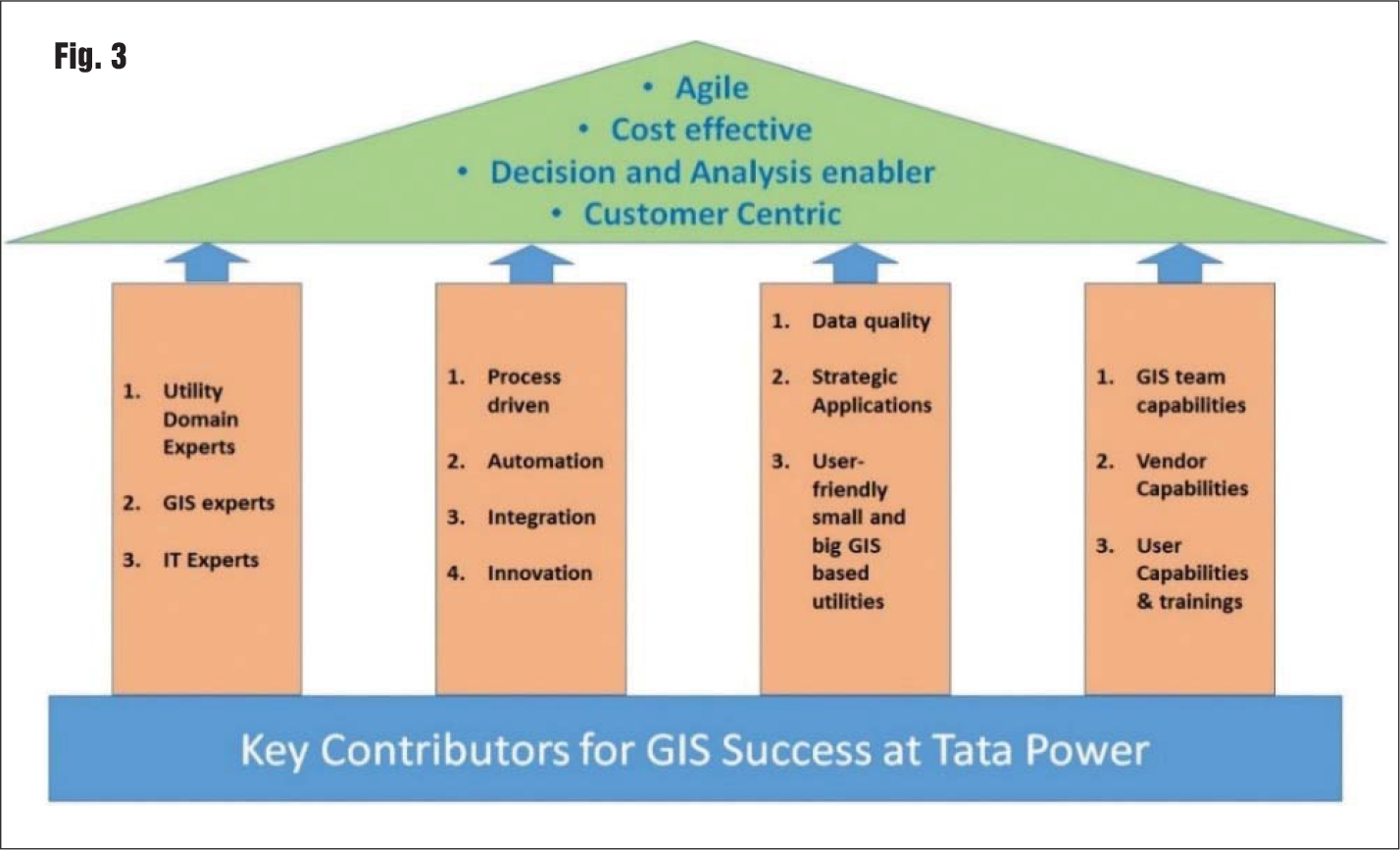
Conclusion
Tata Power is implementing GIS as an enterprise system. Due diligence, exhaustive requirement studies, a clear balance between “wish” and “necessity”, strategic deployment, and top to bottom ownership have been critical for the successful deployment of GIS at Tata Power. It has become the backbone for Tata Power Distribution. The future is all about technology-based secure and convenient solutions along with AI, big data, AR, etc., and Tata Power is working towards making its systems robust to enhance business intelligence and bring in operational and execution excellence. GIS has emerged as a key digitalisation enabler and a differentiator for Tata Power Distribution.
