Substations and switchgear are critical components of transmission and distribution (T&D) systems and work in close conjunction with each other. The reliability of a power system directly depends on the efficient functioning of its equipment, especially in the wake of greater integration of variable renewable energy with the grid. Substations transform the voltage from high to low and house the various equipment required for transformation, switching, regulation and protection of T&D systems. The switchgear comprises devices associated with power system control and protection such as switches, fuses, circuit breakers and relays.
Switchgear classification
The technology and range of switchgear varies across different segments of the grid, depending on the voltage level. Based on the load-bearing capacity, the market for switchgear in India is categorised into three segments – low voltage (LV), medium voltage (MV) and high voltage (HV). The LV switchgear segment includes switchgear rated up to 1 kV, the MV segment consists of switchgear rated up to 33 kV, and the HV segment includes devices rated at 66 kV and above. The key consumer segments of LV switchgear include distribution utilities, industries, residential and commercial buildings, and agricultural consumers. Common LV switchgear devices include air circuit breakers (ACBs), moulded case circuit breakers (MCCBs), motor protection circuit breakers (MPCBs), miniature circuit breakers (MCBs), residual current devices (RCDs), switch fuse (S/F) and fuse switch (F/S) units, high rupturing capacity (HRC) fuses, thermal overload and protection relays, contactors, starters, distribution boards and switches.
MV and HV switchgear is often categorised as one owing to its usage and applications, which are mainly in power systems. For the MV and HV segment, transmission and generation utilities are the key users. Depending on the insulating medium, HV switchgear is classified into three major types – air-insulated switchgear (AIS), gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) and hybrid switchgear. Substations equipped with these are also classified accordingly, that is, AIS substations, GIS substations and hybrid substations.
Market size
The overall domestic market size is estimated at Rs 195 billion as of 2016-17, of which LV switchgear accounts for nearly 75 per cent, while the rest is accounted for by MV and HV switchgear. LV switchgear has a major share in the overall switchgear market owing to increased demand from the commercial and residential sectors. In the MV/LV segment, AIS holds a major market share; however, the share of GIS is steadily increasing.
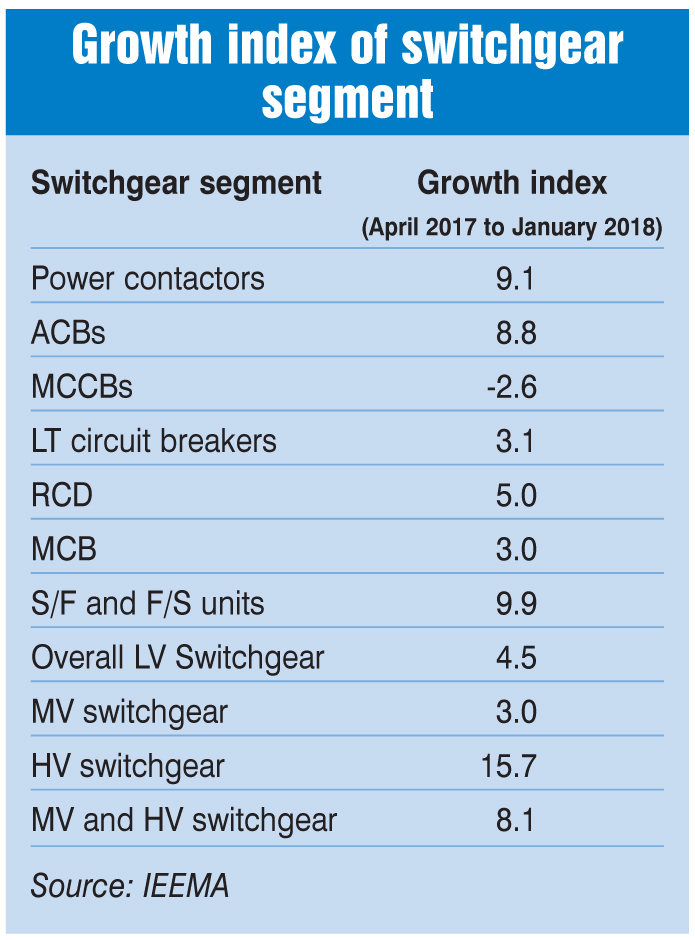
As per the Indian Electrical Equipment Manufacturers Association (IEEMA), switchgear is the second biggest segment in the Indian electrical equipment industry next only to wires and cables. The switchgear segment accounts for over 19 per cent weightage (LV 14 per cent, MV and HV 5 per cent) in the overall electrical equipment industry in the country. The growth index of the LV, MV and HV switchgear segments stood at 4.5 per cent, 3 per cent and 15.7 per cent respectively for the April 2017-January 2018 period. All equipment in the LV and HV switchgear categories (including contactors, ACBs, circuit breakers, RCDs, MCBs, S/F and F/S units) recorded growth, except MCCBs, which registered a decline of 2.6 per cent.
Import-export trend
The import-export trend of switchgear equipment has been very dynamic. In 2016-17, the import of HV switchgear recorded a significant 70 per cent increase over the previous year whereas exports recorded a 5.3 per cent increase. However, during the period April 2017 to January 2018, the import of HV switchgear declined steeply by 24 per cent, while exports increased by 6 per cent. In the LV switchgear segment, imports and exports grew by 18 per cent and 4.7 per cent respectively in 2016-17. Meanwhile, between April 2017 and January 2018, imports increased by 14 per cent and exports declined by 4 per cent.
Owing to an increasing focus on conserving right of way and ensuring uninterrupted power supply, utilities are focusing on substation and switchgear technologies that require less space and have a reduced outage. Conventionally, utilities installed AIS substations, which use air for insulation between various live parts, but now GIS substations, which use sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) gas as the insulating medium, are picking up pace owing to their reduced space requirement and higher uptime. As per the Central Electricity Authority, GIS substations require 35 per cent less space than AIS substations, and have lower maintenance and outage costs. Although the initial cost of GIS substations is about 50 per cent higher than that of their AIS counterparts, the overall capital costs are comparable if the cost of land is also included.
As per Tarang, over 67,000 MVA of GIS substations are currently under construction in the country and slated for commissioning until 2021. Of this, Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (Powergrid) is implementing nearly 17,000 MVA of GIS substations. Among state transcos that have significant capacities lined up are Tamil Nadu Transmission Corporation Limited (9,745 MVA), the Gujarat Energy Transmission Company (7,740 MVA) and Delhi Transco Limited (7,500 MVA).
Utilities can also opt for a hybrid switchgear-based substation, which is a mix of AIS and GIS technologies. In a hybrid substation, the busbars are air-insulated and all other equipment such as circuit breakers, bushings, busducts, connecting elements, disconnectors, current transformers and sensors are gas insulated. The initial cost of hybrid substations is 20 per cent higher than that of AIS, and these substations require a moderate size of land (about 50 per cent less than AIS and 50 per cent more than GIS).
Ultra high voltage (UHV)/Extra high voltage (EHV) switchgear and smart switchgear are the other key emerging technology trends. The growing demand for greater transmission of power over longer distances and with lower losses necessitates the move to UHV/EHV transmission technologies at 800 kV, 1,100 kV and 1,200 kV. In recent years, Powergrid has commissioned the ±800 kV 6,000 MW North East Agra UHDC link, ±800 kV 6,000 MW Champa-Kurukshetra Bipole and the 1,200 kV UHVAC Bina National Test Station. It is currently executing the ±800 kV Raigarh-Pugalur UHVDC link. These large UHV power systems require switchgear that can meet stringent safety, performance and reliability demands. UHV AIS and GIS substations equipped with advanced equipment such as fibre optic current sensors and UHV dead tank circuit breakers and interrupters are deployed in such projects.
With the increasing integration of renewable energy into the grid, there is a need for smart switchgear solutions that provide better monitoring and control capabilities. To meet this demand, smart internet of things (IoT)-ready switchgear solutions are coming up, which can connect to the internet to provide real-time monitoring, predictive diagnostics and better protection against faults. These switchgear are embedded with intelligent electronic devices and are preprogrammed for the remote monitoring and communication of key electrical parameters like current, voltage, faults, etc. This facilitates the automatic regulation of incoming and outgoing power, transfer of power during peak load, and opening and closing of switches to maintain power load. Smart switchgear can also be seamlessly integrated with energy management, building management, supervisory control and data acquisition and other enterprise-level utility systems to control power flow and achieve energy savings.
The way forward
The substation and switchgear market is set to grow rapidly in the coming years. With over 124,263 ckt. km of transmission lines and about 426,535 MVA of substation capacity under construction (as per the Tarang web page accessed on June 14, 2018), the demand for T&D equipment is expected to remain robust. Various central government schemes aimed at strengthening T&D networks such as the green energy corridors, IPDS and DDUGJY, and at expanding electricity access such as Saubhagya are also playing a key role in spurring equipment demand. The expansion of HVDC and HVAC transmission projects as well as the launch of the smart cities initiative is expected to further drive the demand for advanced substation and switchgear solutions.